A Comprehensive Framework for Progress
Synopsis
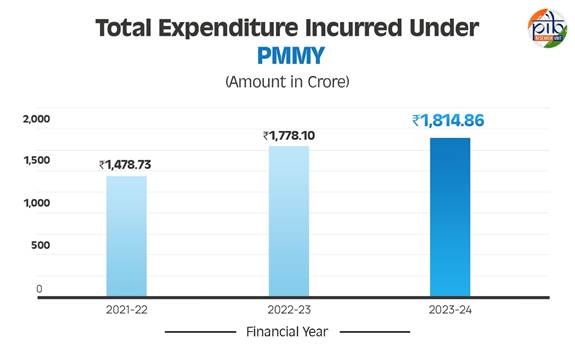
The Ministry of Women and Child Development has spearheaded major initiatives to enhance women’s safety, security, and overall well-being. Key programs like Mission Shakti have supported 10.61 lakh women through One Stop Centres (OSCs), while the Women Helpline (181-WHL) has assisted lakhs of women in distress. Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) has contributed to an improved Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB) from 918 (2014-15) to 930 (2023-24), and Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) of girls in secondary schools has risen from 75.51% to 78% in the same period. For economic empowerment, Sakhi Niwas provides secure accommodation for working women, and Palna ensures daycare support. Nari Adalat offers grievance redressal at the Gram Panchayat level, while SANKALP serves as a resource hub for women’s welfare schemes. The total expenditure incurred under the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) has consistently increased over the years, rising from ₹1,478.73 crore in 2021-22 to ₹1,814.86 crore in 2023-24, reflecting the government’s continued support for micro and small enterprises. Health interventions have also yielded positive results. Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) has dropped from 130 per lakh live births (2014-16) to 97 (2018-20). Mission Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0 supports 9.88 crore beneficiaries, with 6.77 lakh AWCs having their own buildings, 9.93 lakh AWCs with functional toilets, and 12.31 lakh AWCs with drinking water access.
The empowerment of women is a transformative process that ensures women have equal access to opportunities in all areas of life: economic, cultural, social, and political. This not only enhances their individual potential but also contributes to societal progress. India has made remarkable strides in empowering women, focusing on their safety, security, economic independence, and social inclusion. This document outlines some of the key programs driving India’s progress in women’s empowerment, demonstrating the nation’s commitment to creating a more equitable and inclusive society.
Mission Shakti
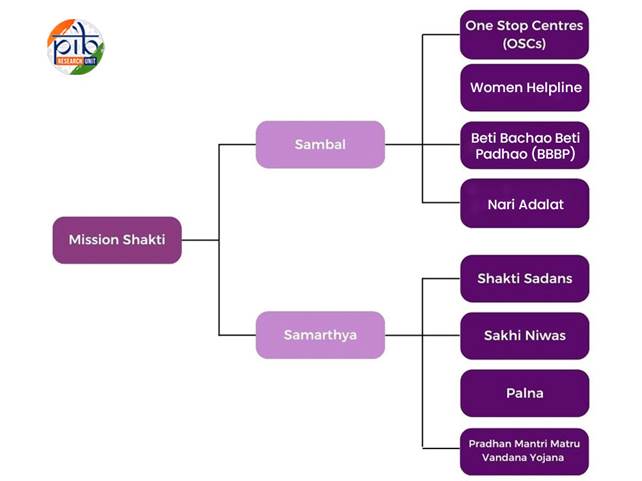
The Ministry has formulated ‘Mission Shakti’, an Integrated Women Empowerment Programme, as Umbrella Scheme for the Safety, Security and Empowerment of Women for implementation during the 15th Finance Commission period from 2021-22 to 2025-26. This initiative has been instrumental in improving the lives of women across the country through its two main verticals: Sambal (for safety and security) and Samarthya (for empowerment).
One Stop Centres (OSCs)
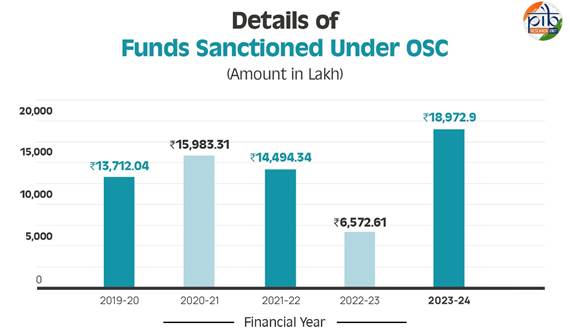
One Stop Centres provides integrated support and assistance under one roof to women affected by violence and those in distress, both in private and public spaces. It provides services like medical aid, legal aid and advice, temporary shelter, police assistance and psycho-social counselling to needy women. Since inception until 31 2024, 10,61,337 women have received assistance through OSCs, demonstrating a significant impact in providing protection and rehabilitation.
Women Helpline (181-WHL)
WHL is a component of Sambal vertical under Mission Shakti, aims to provide 24x7x365 emergency and non-emergency response through telephonic short-code 181 to women, both in public and private spaces by linking them with appropriate authorities such as Police, One Stop Centres, Hospitals, Legal Services Authorities etc. Additionally, it provides information about women welfare schemes and programs.

Data till 31 December 2024
Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP)
BBBP scheme was launched on 22nd January 2015. The scheme aims to prevent gender biased sex selective elimination, ensure survival and protection of girl child and also to ensure education of the girl child.

As per the latest reports of Health Management Information System (HMIS) of Ministry of Health &Family welfare (MoHFW) reveal that SRB is showing improving trends and has increased from 918 in 2014-15 to 930 (Provisional) in 2023-24 at national level. Gross enrollment ratio of girls in the schools at secondary level has increased from 75.51 percent in (2014-15) to 78 percent in (2023-24) [as per UDISE-data, MoE].
Nari Adalat
Nari Adalat aims for providing women with an alternate Grievance Redressal Mechanism for resolving cases of petty nature (harassment, subversion, curtailment of rights or entitlements) faced by them at Gram panchayat level by negotiation, mediation, and reconciliation with mutual consent for speedy, accessible, and affordable justice. It is also used as a platform for awareness of right, entitlements, social facilitation and hand holding of women centric organizations.


Data till 31 December 2024
Shakti Sadans
Shakti Sadan Scheme is an Integrated Relief and Rehabilitation Home for women in distressful situations including trafficked women. It aims at creating a safe and enabling environment for the women in such difficult situations, to enable them to overcome the adverse circumstances.

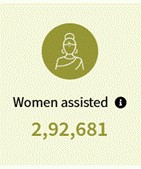
Palna
The Government of India has decided to provide the day-care creche facilities through the component of Palna. Anganwadi centres are the world’s largest childcare institutions dedicated to providing essential care and support to children ensuring delivery of care facilities till the last mile. This will ensure whole day childcare support ensuring their well-being in a safe and secure environment. The objective of Palna component is to provide quality creche facility in safe and secure environment for children.

Data till 31 December 2024
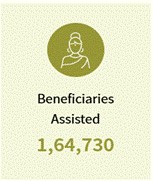
Sakhi Niwas
The objective of the Scheme is to provide safe, secure, conveniently located, and affordable accommodation for women who are in the workforce and/or aspire to join the workforce. The scheme also makes a provision of Day Care Centre for children of the residents of the Sakhi Niwas.

Data till 31 December 2024
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
The Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY) provides financial compensation for loss of wages due to pregnancy and childbirth. The scheme, previously limited to the first child, has now been extended to cover the second child if the child is a girl—a progressive step towards promoting gender equality.
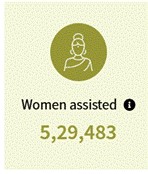
SANKALP
The SANKALP: HEW (Hub for Empowerment of Women) will serve as a vehicle to bridge the information and knowledge gap regarding schemes and facilities available for women as well as guide them to avail the benefits and entitlements. It will also serve as a Project Monitoring Unit (PMU) for all components under Mission Shakti and will work in convergence with the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) scheme.


Data till 31 December 2024
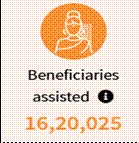
Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0
The Government of India approved “Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0” (also referred to as Mission Poshan 2.0) which is a strategic shift in mission mode to develop practices that nurture health, wellness, and immunity from malnutrition. With 13,99,890 Anganwadi Centers (AWCs) operating across 36 States/UTs and 781 districts, the mission aims to enhance the health, wellness, and immunity of children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers. Supported by 13,31,622 Anganwadi Workers, it ensures nutritional benefits reach 9,88,74,477 eligible beneficiaries. Infrastructure improvements include 6,77,349 AWCs with their own buildings, 9,93,863 with functional toilets, and 12,31,201 with access to drinking water. Additionally, in December 2024, 12,93,863 AWCs operated for at least 15 days, 11,86,509 for at least 21 days, and 8,54,395 for at least 25 days.
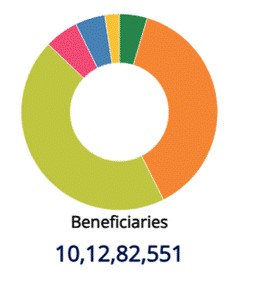
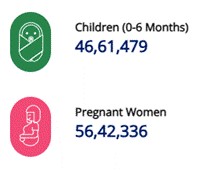


Beneficiaries under Poshan Abhiyaan
Data as on 31 December 2024
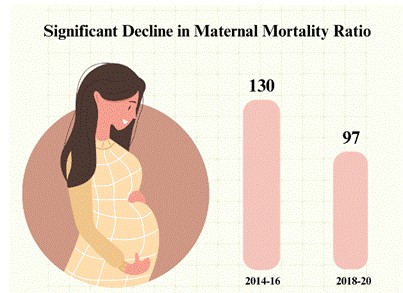
Decreased Maternal Mortality Ratio
India’s Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) has significantly declined from 130 per lakh live births (2014-16) to 97 per lakh live births (2018-20), reflecting improved maternal healthcare services, institutional deliveries, and strengthened healthcare interventions.
Conclusion
The ongoing efforts to promote women’s empowerment have led to tangible improvements in multiple areas, from social and economic participation to access to essential services. By addressing key challenges and ensuring a supportive ecosystem, these measures have played a crucial role in enhancing women’s autonomy and decision-making power. Continued focus on inclusive policies, awareness, and institutional strengthening will be essential in building a more equitable society where every woman can thrive and contribute to the nation’s development.
References
RAJYA SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 2720 Session 266
RAJYA SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 2717 Session 266
Annual Report 2023-24: https://wcd.gov.in/documents/uploaded/1732020683.pdf
https://missionshakti.wcd.gov.in/
LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 1931 session III
*******
Santosh Kumar/ Sarla Meena / Madiha Iqbal